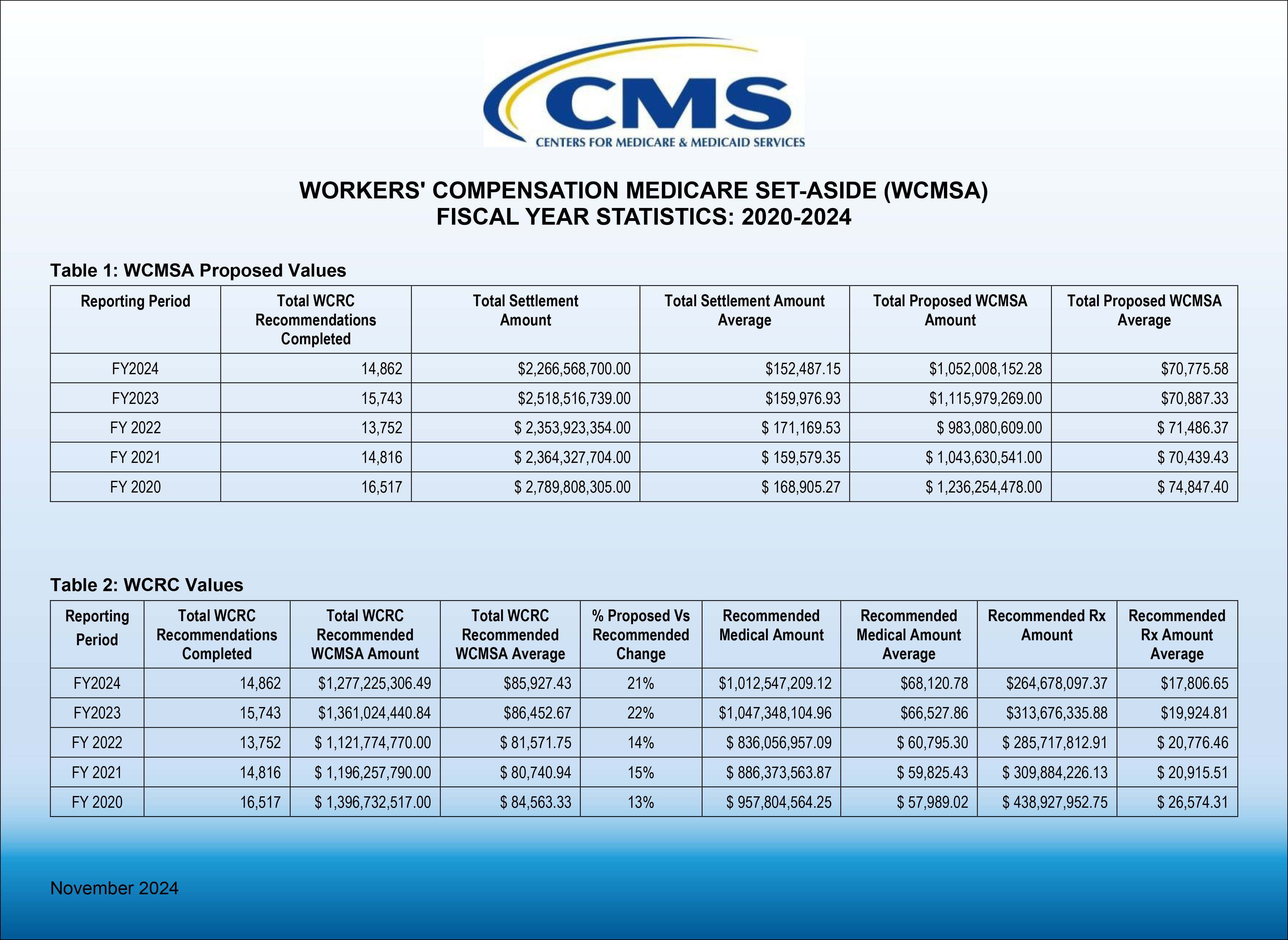
On January 17, 2025, CMS updated its Workers’ Compensation Medicare Set-Aside Arrangement (WCMSA) Reference Guide to reflect a new policy in Section 4.2 to no longer review zero-dollar WCMSAs as of July 2025. Other announced changes in the WCMS Reference Guide, now in version 4.2, include an update of WCRC Review Considerations in Section 9.4.3 and corrected example calculations for Intrathecal Pump, Spinal Cord Stimulator, and Peripheral Nerve stimulator replacements were made in Section 9.4.5.
On January 21, 2025, CMS indicated via email and its website that it will be implementing two operational changes to the WCMSA review process in the first half of 2025 as follows:
“Amended Reviews: Currently, amended review requests cannot be submitted until 1 year after a WCMSA case has been approved. Effective April 7, 2025, amended review requests will be allowed at any time after a WCMSA case is approved.
Zero-Dollar Set-Asides: Effective July 17, 2025, CMS will no longer accept or review WCMSA proposals with a zero-dollar ($0) allocation. Entities should still consider the parameters available in the WCMSA Reference Guide (PDF) to determine whether a zero-dollar WCMSA allocation is appropriate and should maintain documentation to support that allocation.”
As a refresher, the WCMSA Reference Guide, in Section 4.2, which describes when a zero-dollar MSA is appropriate, used to list three conditions to determine when Medicare’s future interests in a Workers’ Compensation settlement had been protected. The Reference Guide’s updated Section 4.2 has been revised significantly, and now includes only two conditions to indicate when Medicare’s future interests are protected in a WC settlement with several examples of when the second condition is met as listed in the text below:
“4.2 Indications That Medicare’s Interests Are Protected
Submitting a WCMSA proposed amount for review is never required. But WC claimants must always protect Medicare’s interests. A WCMSA is not necessary under the following conditions because when they are true, they indicate that Medicare’s interests are already protected:
a) The facts of the case demonstrate that the injured individual is only being compensated for past medical expenses (i.e., for services furnished prior to the settlement); and
b) There is no evidence that the individual is attempting to maximize the other aspects of the settlement (e.g., the lost wages and disability portions of the settlement) to Medicare’s detriment.
These conditions may be demonstrated through one of the following:
• The individual’s treating physician documents in medical records that to a reasonable degree of medical certainty the individual will no longer require any treatments or medications related to the settling WC injury or illness; or
• The workers’ compensation insurer or self-insured employer denied responsibility for benefits under the state workers’ compensation law and the insurer or self-insured employer has made no payments for medical treatment or indemnity (except for investigational purposes) prior to settlement, medical and indemnity benefits are not actively being paid, and the settlement agreement does not allocate certain amounts for specific future or past medical or pharmacy services as a condition of settlement; or
• A Court/Commission/Board of competent jurisdiction has determined, by a ruling on the merits, that the workers’ compensation insurer or self-insured employer does not owe any additional medical or indemnity benefits, medical and indemnity benefits are not actively being paid, and the settlement agreement does not allocate certain amounts for specific future medical services; or
• The workers’ compensation claim was denied by the insurer/self-insured employer within the state statutory timeframe allowed to pay without prejudice (if allowed in that state) during investigation period, benefits are not actively being paid, and the settlement agreement does not allocate certain amounts for specific future medical services.
In addition, if a settlement leaves WC carriers with responsibility for ongoing medical and prescription coverage once the settlement funds are fully spent, then a WCMSA is not necessary.
Effective July 17, 2025, CMS will no longer accept or review WCMSA proposals with a zero- dollar ($0) allocation. Entities should consider the above parameters in determining whether a zero-dollar WCMSA allocation is appropriate and maintain documentation to support that allocation.
Notes:
… If Medicare made any conditional payments for WC injury-related services furnished prior to settlement, then Medicare will recover those payments. In addition, Medicare will not pay for any WC injury-related services furnished prior to the date of the settlement for which it has not already paid.
CMS will not issue “verification letters” stating that a WCMSA is not necessary.
In instances where the above conditions are not met, CMS’ voluntary, yet recommended, WCMSA amount review process is the only process that offers both Medicare beneficiaries and Workers’ Compensation entities finality, with respect to obligations for medical care required after a settlement, judgment, award, or other payment occurs. When CMS reviews and approves a proposed WCMSA amount, CMS stands behind that amount. Without CMS’ approval, Medicare may deny related medical claims, or pursue recovery for related medical claims that Medicare paid up to the full amount of the settlement, judgment, award, or other payment.”
The second to last paragraph of Section 9.4.3 was substituted from:
“The WCRC relies on evidence-based guidelines for prescription medication and medical treatment allocations; however, these are guidelines, not rules. The final determination is also based on the claimant’s past use and future recommended treatment as supported by the medical records and by current peer-reviewed medical literature. See Appendix 4 for a list of resources the WCRC uses.”
to the following:
“The WCRC final determination relies on the claimant’s past use and future recommended treatment as supported by the medical records. Evidence-based guidelines for prescription medication and medical treatment allocations and current peer-reviewed medical literature are also reviewed; however, these are guidelines, not rules. See Appendix 4 for a list of resources the WCRC uses. Treating provider plans are given preference where the two are at odds.”
The corrected example calculations in 9.4.5 for intrathecal (IT) pump pricing should be reviewed by allocators and their price coders to make sure that WCMSA pricing for IT pumps is consistent with the corrected calculations in the updated Reference Guide.
Take Aways:
• The new “no review” policy for zero-dollar MSA’s seems driven in large part to spirited feedback provided to CMS from the WCMSA community. There were several CMS panel discussions with MSP Network membership at the September 2024 MSP Network educational conference in Baltimore during which many of the concerns now addressed in updated Section 4.2 of the Reference Guide concerning WC cases with no payments toward denied body parts (other than during investigation periods), determinations made by WC judges/commissions at the state level, and statutory limits on payment of future medicals by WC carriers were brought up and debated.
• The drop of the one year waiting period before submitting Amended Reviews is another step toward more fair reviews by CMS and also seems to be a result of strong advocacy by those who submit allocation reports, the attorneys, who represent those entities, and the MSP Network stakeholder community at large.
• This is encouraging as it shows that CMS does listen to feedback from the MSP stakeholder community.
For Additional Information
Medivest will continue to monitor changes occurring at CMS and will keep its readers up to date when such changes are announced. For questions, feel free to reach out to the Medivest representative in your area by clicking here or call us direct at 877.725.2467.